A zone of inhibition means the bacteria is inhibited by the antimicrobial.
The Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method is a type of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Antimicrobial-saturated paper discs are placed onto a culture plate inoculated with pure growth of the bacteria of interest. The plates are evaluated at 24 hours and the zones of inhibition around each disc measured.
The measured zones of inhibition are compared to “breakpoints” (previously established zones) for each antimicrobial for that bacteria. This determines whether the bacteria is susceptible, resistant, or somewhere in between (“intermediate”) to that antimicrobial.
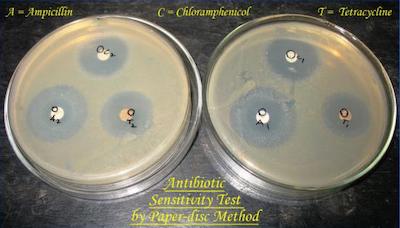
This allows the clinician to choose an appropriate antimicrobial to which the bacteria are susceptible.
Other methods: the broth dilution and microbroth dilution methods both measure the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The MIC is the smallest amount of antimicrobial that inhibits growth of the bacteria being evaluated.
Ref: Bassert, Beal and Samples, McCurnin’s Clinical Textbook for Veterinary Technicians, 9th ed. pp. 467-70. Image courtesy of Sudipta.nov15.

